IMU signals
This example demonstrates how to log multi dimensional signals with the Rerun SDK, using the TUM VI Benchmark.
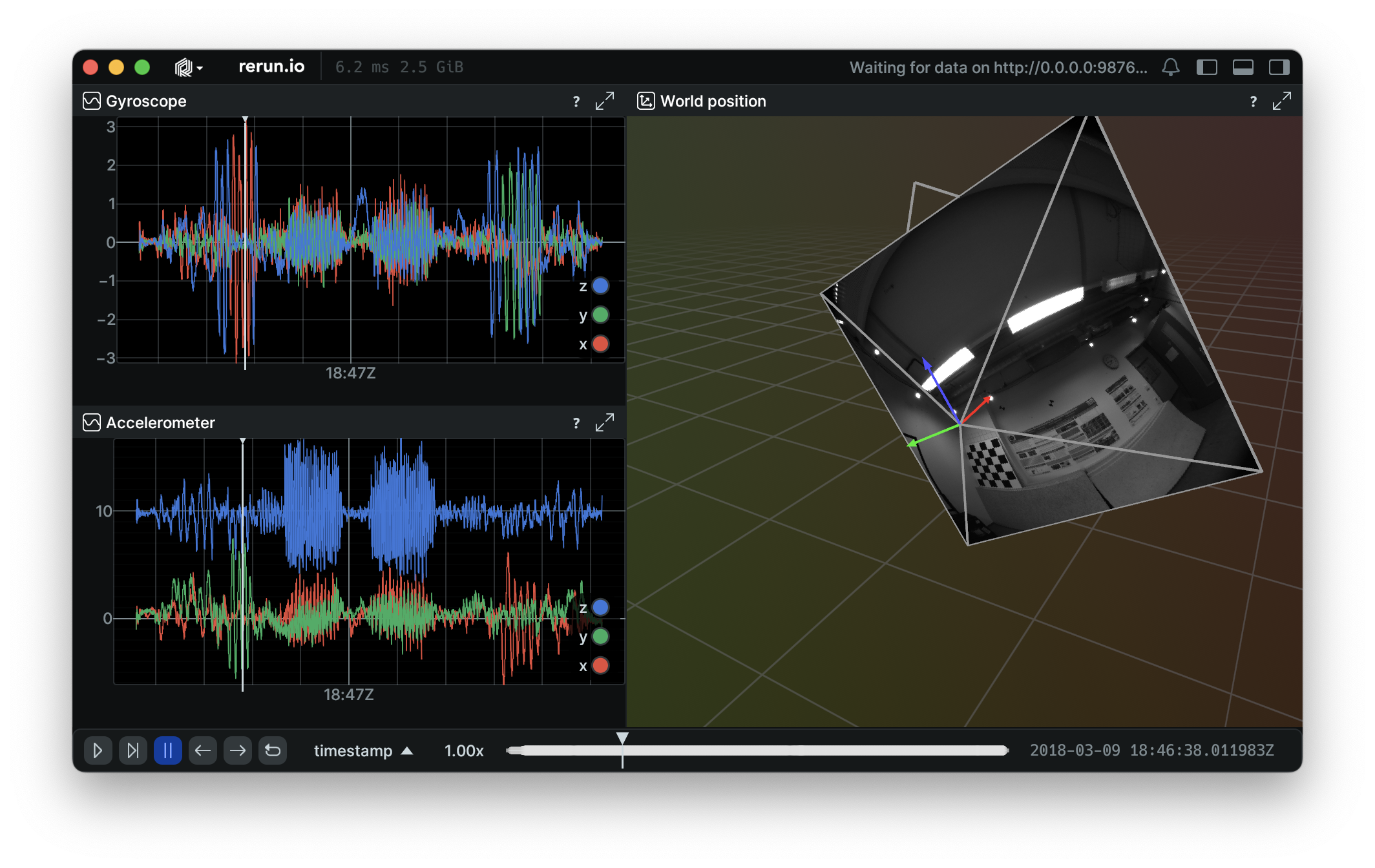
Background background
This example shows how to log multi-dimensional signals efficiently using the rr.send_columns() API.
The API automatically selects the right partition sizes, making it simple to log scalar signals like this:
# Load IMU data from CSV into a dataframe
imu_data = pd.read_csv(
cwd / DATASET_NAME / "dso/imu.txt",
sep=" ",
header=0,
names=["timestamp", "gyro.x", "gyro.y", "gyro.z", "accel.x", "accel.y", "accel.z"],
comment="#",
)
times = rr.TimeColumn("timestamp", timestamp=imu_data["timestamp"])
# Extract gyroscope data (x, y, z axes) and log it to a single entity.
gyro = imu_data[["gyro.x", "gyro.y", "gyro.z"]]
rr.send_columns("/gyroscope", indexes=[times], columns=rr.Scalars.columns(scalars=gyro))
# Extract accelerometer data (x, y, z axes) and log it to a single entity.
accel = imu_data[["accel.x", "accel.y", "accel.z"]]
rr.send_columns("/accelerometer", indexes=[times], columns=rr.Scalars.columns(scalars=accel))Running running
Install the example package:
pip install -e examples/python/imu_signalsTo experiment with the provided example, simply execute the main Python script:
python -m imu_signalsAttribution attribution
This example uses a scene from the TUM VI Benchmark dataset, originally provided by Technical University of Munich (TUM). The dataset is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 (CC BY 4.0).
- Original dataset: TUM VI Benchmark
- License details: CC BY 4.0